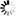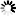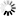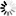FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖
FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖
Chemical names: FITC-羧甲基-葡聚糖;Fluorescein- thiocarbamoyl-(O-carboxymethyl)-dextran
Trade name: FITC-CM-dextran
Trade name: FITC-CM-dextran
FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖是帶有羧甲基取代基的FITC標記葡聚糖。為了研究細胞和細胞膜,開發了FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖。羧甲基基團使產品帶有負電荷。檢查每個批次的分子量,取代度,干燥失重和游離FITC。TdB生產分子量范圍從4KDa到150KDa的 FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖。 FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖呈橙黃色粉末。
結構與性質
FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖是由選定的葡聚糖組分與活化的羧甲基衍生物在堿性條件反應制備,O-羧甲基基團也因此被接到糖鏈上。羧甲基的含量大約是5%,相當于每5個葡萄糖單元上接1個羧甲基基團。然后,通過和熒光素異硫氰酸酯反應,接入熒光素(FITC)基團。FITC的取代度在0.003–0.008之間。FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖呈橙黃色粉末,極易溶于水或電解質溶液。由于具有負電荷的羧基基團,該產品具有明顯的聚陰離子性能。FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖的溶液性質與羧甲基葡聚糖性質相當(1-3)。在中性溶液中,羧甲基取代基相互排斥,導致葡聚糖鏈膨脹。FITC-CM葡聚糖不溶于大多數有機溶劑,例如乙醇、甲醇、丙酮、氯仿、乙酸乙酯。

圖 1. FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖的結構式
賴氨酸葡聚糖 (or Dextran-lysine-fixable) 是由來自腸系膜白串珠菌的葡聚糖的特定片段通過賴氨酸標記而合成的。然后用FITC在溫和條件下功能化得到FITC標記賴氨酸葡聚糖。經純化,控制產品的分子量,外觀,溶解度,取代度,pH,游離賴氨酸和游離FITC。產品的分子量是由對應的葡聚糖片段的相近分子量來確定的。例如,FITC標記賴氨酸葡聚糖4的分子量大約為4000 Da。實際分子量是通過GPC測定的。葡聚糖來源于腸系膜白串珠菌B-512F,由α-D-(1-6)線性葡聚糖組成, α-(1-3) 側鏈含量較低(2-5%)。葡聚糖的分子量范圍從4000 到500000,并且通過GPC,比旋,吸光率和其它參數嚴格控制質量。

圖2. FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖在0.025M硼酸鹽緩沖溶液(10mg溶于50 ml緩沖液pH9.0)的熒光圖譜。
激發波長493nm;發射波長519nm
儲存和穩定性
已開展的穩定性預期研究證實,羧甲基葡聚糖至少在3年內保持其效力和純度(未發表的研究)。根據我們對FITC標記葡聚糖的經驗,推測FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖具有類似的穩定性。建議將FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖儲存在密閉容器中,在室溫下避光保存,可保存6年。
應用
FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖主要用于滲透性和微循環研究。羧基賦予分子一個負電荷,這或有助于獲取細胞膜和組織滲透特性信息。游離羧基也可用于將其他物質與葡聚糖鏈偶聯。
羧甲基葡聚糖被發現具有生物相容性,用作一些藥物和診斷應用的起始原料。FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖的毒性預期很低。在葡聚糖鏈中接入羧基,為將具備有趣生物活性的分子(藥物、酶、診斷示蹤劑)固定在葡聚糖上提供了進一步機會。羧基部分可用于許多反應,例如酯化、和胺發生酰胺化、UGI反應或Passerini反應。簡單的離子結合反應也可以提供一系列包含不同陽離子分子(4,5)的衍生物。羧基還將賦予分子整體負電荷,這可能有助于獲得有關細胞膜和組織的滲透特性的信息(6)。FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖在藥物傳遞系統研究中的應用也見諸報道(7)。
產品列表
|
產品編號
|
品名
|
分子量(kDa)
|
包裝
|
|
FITC-CM-dextran 4
|
4
|
100 mg
|
|
|
1 g
|
|||
|
FITC-CM-dextran 20
|
20
|
100 mg
|
|
|
1 g
|
|||
|
FITC-CM-dextran 40
|
40
|
100 mg
|
|
|
1 g
|
|||
|
FITC-CM-dextran 70
|
70
|
100 mg
|
|
|
1 g
|
|||
|
FITC-CM-dextran 150
|
150
|
100 mg
|
|
|
1 g
|
參考文獻
1. K. Gekko, Solution properties of dextran and its ionic derivatives, ACS Symposium Series, 150(1981), 415-438.
2. K. Gekko and H. Noguchi, Selective interaction of calcium and magnesium ions with ionic dextran derivatives, Carbohydr Res, 69(1979), 323-326.
3. O.Smidsröd and A.Haug, Estimation of the relative stiffness of the molecular chain in polyelectrolytes from measurements of viscosity at different ionic strengths, Biopolymers, 10(1971), 1213-27.
4. P. Rongved and J. Klaveness, Water soluble polysaccharides as carriers of paramagnetic contrast reagents for magnetic resonance imaging; Synthesis and relaxation properties, Carbohydr Res, 214(1991), 315-323.
5. S.W Zheng, M. Huang et al., RGD-conjugated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement and hyperthermia, magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement and hyperthermia, J Biomater Appl, 28(2014), 1051-1059.
6. D. Asgiersson, D. Venturoli, B. Rippe and C. Rippe, Increased glomerular permeability to negatively charged polysucrose relative to neutral polysucrose in rats, Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 291(2006), F1083-9.
7. C. Martin, E .Dolmazon, K. Moylan et al., A charge neutral tuneable polymersome capable of high biological encapsulation efficiency and cell permeation, Int J Pharmaceutics, 481(2015), 1-8.
2. K. Gekko and H. Noguchi, Selective interaction of calcium and magnesium ions with ionic dextran derivatives, Carbohydr Res, 69(1979), 323-326.
3. O.Smidsröd and A.Haug, Estimation of the relative stiffness of the molecular chain in polyelectrolytes from measurements of viscosity at different ionic strengths, Biopolymers, 10(1971), 1213-27.
4. P. Rongved and J. Klaveness, Water soluble polysaccharides as carriers of paramagnetic contrast reagents for magnetic resonance imaging; Synthesis and relaxation properties, Carbohydr Res, 214(1991), 315-323.
5. S.W Zheng, M. Huang et al., RGD-conjugated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement and hyperthermia, magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement and hyperthermia, J Biomater Appl, 28(2014), 1051-1059.
6. D. Asgiersson, D. Venturoli, B. Rippe and C. Rippe, Increased glomerular permeability to negatively charged polysucrose relative to neutral polysucrose in rats, Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 291(2006), F1083-9.
7. C. Martin, E .Dolmazon, K. Moylan et al., A charge neutral tuneable polymersome capable of high biological encapsulation efficiency and cell permeation, Int J Pharmaceutics, 481(2015), 1-8.
返回FITC標記多糖
西寶生物專業提供TdB葡聚糖及其衍生物、熒光標記多糖等產品,歡迎來電400-021-8158垂詢!
 |
 |
 |
| 官網:www.baichuan365.com | 微信服務號:iseebio | 微博:seebiobiotech |
 |
 |
 |
| 商城:mall.seebio.cn | 微信訂閱號:seebiotech | 泉養堂:www.canmedo.com |
下一篇:FITC標記羧甲基聚蔗糖上一篇: FITC標記賴氨酸葡聚糖
此文關鍵字:FITC標記羧甲基葡聚糖
相關資訊
- 糖尿病轉基因豬模型建立
- NBB培養基-Dollar 德樂品牌
- Nat Com:最新研究找到調節心臟及肌肉關鍵蛋白的機理
- 西寶生物攜新品Krovin防腐劑亮相慕尼黑上海分析生化展(analytica China 2018)
- Galacturonan 半乳糖醛酸/ Apiogalacturonan 芹半乳糖醛酸 - Elicityl生物質提取天然多糖和寡糖產品(10)
- Science:巨噬細胞竟是維持乳腺干細胞的“搖籃”
- 多糖分析HPLC柱和緩沖溶液 - Ludger糖基化產品
- 【每周優選】食品過敏原快速檢測試劑盒
- Alginate 海藻酸 - Elicityl生物質提取天然多糖和寡糖產品(9)
- 巨噬細胞是幫助心臟修復甚至再生的關鍵
新進產品
同類文章排行
- 汽巴藍3G-A(Cibacron Blue 3G-A)
- 異硫氰酸熒光素 (FITC)
- TdB染料
- 透明質酸衍生物 Hyaluronic acid derivatives
- 聚蔗糖 Polysucrose
- 季胺標記葡聚糖 Q-Dextran
- 苯基標記葡聚糖 Phenyl-dextran
- 賴氨酸標記葡聚糖 Lysine-Dextran
- 羧甲基標記聚蔗糖 CM-Polysucrose
- 羧甲基標記葡聚糖 CM-Dextran
資訊文章
您的瀏覽歷史